一、认识Vuejs
1.1 Vue是一个渐进式的框架。
1.1.1 渐进式:
渐进式意味着你可以将Vue作为你应用的一部分嵌入其中,带来更丰富的交互体验。
或者如果你希望将更多的业务逻辑使用Vue实现,那么Vue的核心库以及其生态系统。
比如Core+Vue-router+Vuex,也可以满足你各种各样的需求。
1.2 第一个Vue实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//let(变量)/const(常量)
//编程范式:声明式编程
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',//用于挂载要管理的元素
data: {//定义数据
message: '你好!'
}
})
//元素js的做法(编程范式:命令式编程)
//1.创建div元素,设置id属性
//2.定义一个message变量
//3.将message变量放在前面的div元素中显示
//4.修改message数据,并替换
</script>
</body>
</html>1.3 第二个Vue实例-列表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies"></li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
messages: '你好啊',
movies: ['魔界契约', '海王', '哪吒', '盗墓笔记']
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1.4 第三个Vue实例-计数器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>当前计数:</h2>
<!-- v-on监听-->
<!-- <button v-on:click="counter++">+</button>-->
<!-- <button v-on:click="counter--">-</button>-->
<button v-on:click="add">+</button>
<button @click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//语法糖:简写 @click是v-on:click的语法糖
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
counter: '0'
},
methods: {
add: function () {
console.log('add被执行')
this.counter++
},
sub: function () {
console.log('sub被执行')
this.counter--
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1.5 MVVM
Model View ViewModel
- View层:
- 视图层
- 在我们前端开发中,通常就是DOM层。
- 主要的作用是给用户展示各种信息。
- Model层:
- 数据层
- 数据可能是我们固定的死数据,更多的是来自我们服务器,从网络上请求下来的数据。
- 在我们计数器的案例中,就是后面抽取出来的obj,当然,里面的数据可能没有这么简单。
-
VueModel层:
- 视图模型层
- 视图模型层是View和Model沟通的桥梁。
- 一方面它实现了Data Binding,也就是数据绑定,将Model的改变实时的反应到View中
- 另一方面它实现了DOM Listener,也就是DOM监听,当DOM发生一些事件(点击、滚动、touch等)时,可以监听到,并在需要的情况下改变对应的Data。
1.6 开发中什么是函数,什么是方法?
1.7 vue的生命周期
初始化->更新->死亡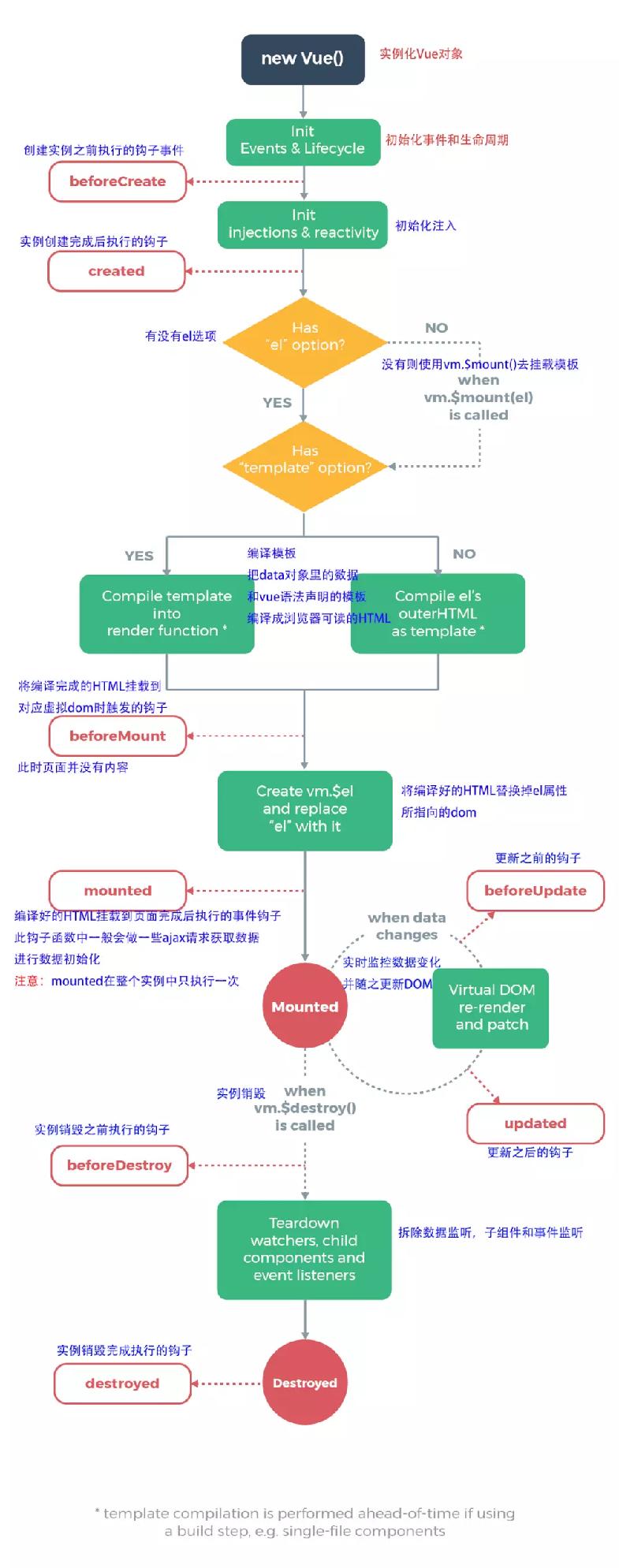
1.8 模板语法
1.8.1 Mustache语法(双括号):可以使用简单的表达式
1.8.2 v-once:只渲染一次,之后不会随数据更改,并且后面不跟表达式
1.8.3 v-html:设置有标签的超链接
1.8.4 v-text:类似于Mustache语法,但不可拼接,使用较少
1.8.5 v-pre:原封不动的显示标签内的内容,不用解析
1.8.6 v-cloak:在vue解析之前有效,避免显然出未编译的Mustache标签
1.8.7 v-bind:
1.9 计算属性
1.9.1 计算属性的定义:
把数据进行一些转化后再显示,或者把多个数据结合起来进行显示
1.9.2 计算属性的案例:
案例一:firstName+lastName
案例二:books->price
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>计算属性复杂操作</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>总价格:</h2>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
books: [
{id: 110, name: 'Vue框架', price: 120},
{id: 111, name: '一行代码', price: 69},
{id: 112, name: '操作系统', price: 100},
{id: 113, name: '代码大全', price: 70}
]
},
//computed计算属性
computed: {
totalPrice: function () {
let result = 0
for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) {
result += this.books[i].price
}
return result
}
},
methods: {}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>计算属性完整写法:
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: 'jerry',
lastName: 'tom'
},
//computed计算属性
// 属性一般没有set方法,只读属性
computed: {
fullName: {
set: function (newValue) {
// 截取拿到结果的字符串并赋值
const name = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = name[0]
this.lastName = name[1]
},
get: function () {
return this.firstName+' '+this.lastName
}
}
},
methods: {}
})
</script>1.9.3 计算属性的缓存:
计算属性性能比方法更高,因为计算属性有缓存,执行时只调用一次,而方法用几次调用几次
1.10 事件监听
1.10.1 v-on
定义:绑定事件监听器,语法糖为'@监听事件'
1.10.2 v-on参数问题
1.10.3 v-on修饰符
1.10.4 v-if和v-show区别
v-if当条件为false时,压根不会有对应的元素在DOM中。
v-show当条件为false时,仅仅是将元素的display属性设置为none而已。
当需要在显示与隐藏之间切片很频繁时,使用v-show
当只有一次切换时,通过使用v-if
1.10.5 遍历循环
使用v-for时最好加上key,为了更好的复用1.10.5.1 遍历数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-for遍历数组</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 1.在遍历的过程中,没有使用索引值-->
<ul>
<li v-for="item in names"></li>
</ul>
<!-- 2.在遍历的过程中,获取索引值-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in names">NaN.</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
names: ['why', 'Mois', 'Tom', 'Jerry']
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1.10.5.2 遍历对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-for遍历对象</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 1.在遍历的过程中,如果只是获取一个值,那么获取的是value-->
<ul>
<li v-for="item in info"></li>
</ul>
<!-- 2.获取key和value (value,key)-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,key) in info">:</li>
</ul>
<!-- 3.获取key、value和index-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,key,index) in info">:-</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
info: {
name: 'Mois',
age: 20,
height: 1.88
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1.10.5.3 v-for中最好加入key,但key不能是index(index会有变化)
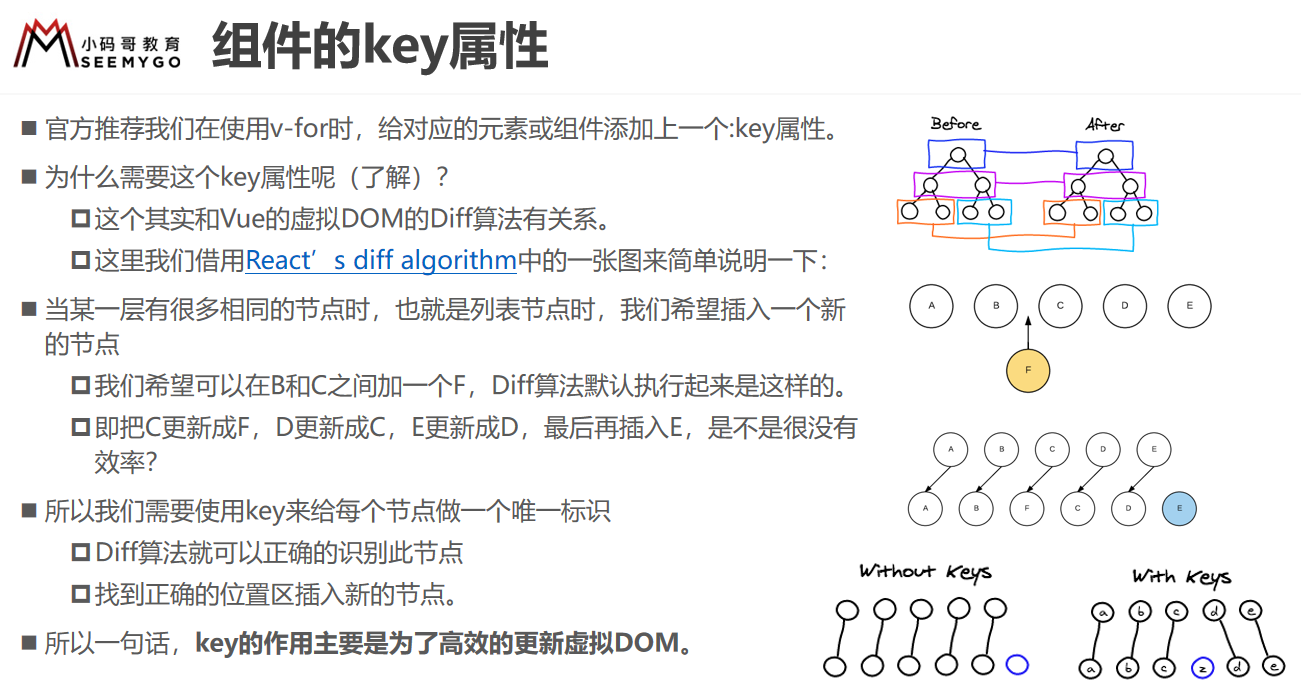
1.10.6 响应方法
观察数组编译的方法,使用它们改变数组也会触发视图的更新。删除元素splice(开始位置),删除除开始位置后的元素
替换元素,splice(start,替换几个元素,‘替换的元素’,‘替换的元素’)
插入元素,splice(开始元素,0,‘插入的元素’,‘插入的元素’)
1.11 书籍购物车的案例
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="books.length">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in books">
<td>book.id</td>
<td>book.name</td>
<td>book.data</td>
<td>book.price|showPrice</td>
<td>
<button @click="decrement(index)" v-bind:disabled="book.count<=1">-</button>
<button @click="increment(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>
<button @click="removeHandler(index)">移除</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h2>总价格:totalPrice|showPrice</h2>
</div>
<div v-else>
<h2>购物车为空</h2>
</div>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="main.js"></script>
<script>
</script>
</body>
</html>main.js
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
books: [
{
id: 1,
name: '《算法导论》',
data: '2019-03-12',
price: 89.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 2,
name: '《UNIX编程艺术》',
data: '2018-07-13',
price: 49.00,
count: 5
},
{
id: 3,
name: '《编程珠玑》',
data: '2020-01-12',
price: 85.00,
count: 11
},
{
id: 4,
name: '《代码大全》',
data: '2020-03-22',
price: 109.00,
count: 2
},
]
},
methods: {
//价格格式化
getFinalPrice(price) {
return '¥' + price.toFixed(2)
},
increment(index) {
this.books[index].count++
},
decrement(index) {
this.books[index].count--
},
removeHandler(index) {
this.books.splice(index, 1)
}
},
// 计算属性
computed: {
totalPrice() {
let totalPrice = 0
//1.普通for循环
for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) {
totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count
}
return totalPrice
// 2.for(let i in this.books)
//3.for(let i in/of this.books)
}
},
//过滤器
filters: {
showPrice(price) {
return '¥' + price.toFixed(2)
}
}
})style.css
table {
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
th, td {
padding: 8px 16px;
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
text-align: left;
}
th {
background-color: #f7f7f7;
color: #5c6b77;
font-weight: 600;
}


